

Photosynthesis is a process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy.
Photosynthesis converts light energy to the chemical energy of sugars and other
organic compounds. This process consists of a series of chemical reactions that require
carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) and store chemical energy in the form of sugar.
Light energy from light drives the reactions. Oxygen (O2) is a by-product of photosynthesis
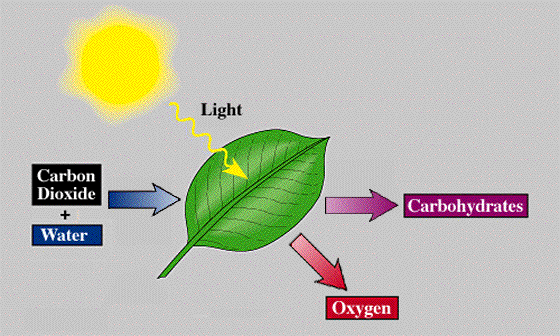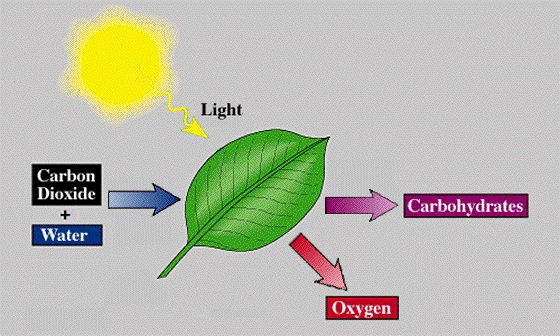
and is released into the atmosphere. The following is an example of how photosynthesis
occurs and the materials needed for it to occur. As you can see, the light from the sun
and carbon dioxide and water react with the leaf (rather the chlorophyl inside the leaf) for
the plant to photosynthesize food. The reaction also releases oxygen and carbohydrates into the
atmosphere.
 The equation for the process is:
The equation for the process is:





